Viscometer vs. Rheometer: Understanding the Key Differences
Advertisement
When it comes to measuring the flow properties of materials, two instruments often come into play: the viscometer and the rheometer. While they both deal with viscosity, there are significant differences between them. Let’s explore what makes each unique.
What is a Viscometer?
A viscometer is an instrument designed to measure the viscosity of a fluid. It provides a reading of how resistant a fluid is to flow.
-
Limited Shear Rate Range: Viscometers typically measure viscosity over a limited range of shear rates. This means they are most accurate within specific flow conditions.
-
Measures Viscosity: The primary function of a viscometer is to determine the viscosity of a fluid.
-
Single Flow Condition: Viscometers generally operate under one flow condition at a time.
-
Various Types: There are several types of viscometers, each suited for different applications. These include:
- Rotational viscometers
- Vibrational viscometers
- Oscillation viscometers
- Falling piston viscometers
- Falling sphere viscometers
- Saybolt viscometers
- Capillary tube viscometers
- Orifice type viscometers
- Redwood viscometers

Figure 1: An example of a falling sphere viscometer
What is a Rheometer?
A rheometer is a more advanced instrument that measures a broader range of flow properties than a viscometer. It measures not just viscosity but also the viscoelasticity of fluids, semi-solids, and even solids.
-
Wide Shear Rate Range: Rheometers measure viscosity over a much wider range of shear rates, making them suitable for complex fluids with varying flow behaviors.
-
Measures Rheological Properties: Rheometers are used to determine the rheological properties of a substance, which include its viscosity, elasticity, and other flow behaviors.
-
Complex Fluids: They are particularly useful for liquids whose viscosities change with flow conditions.
-
Diverse Types: Rheometers also come in various forms, including:
- Rotational rheometers
- Extensional rheometers
- Capillary rheometers
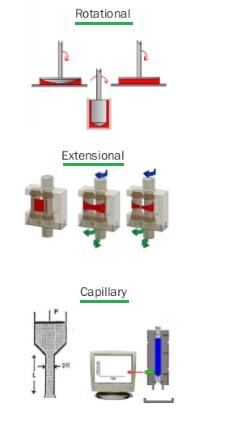
Figure 2: Examples of different rheometer types
Key Differences Summarized
Here’s a concise breakdown of the differences:
- Scope of Measurement: A viscometer measures viscosity, whereas a rheometer measures rheological properties (including viscosity and viscoelasticity).
- Shear Rate Range: Viscometers have a narrower shear rate range, while rheometers have a much wider range.
- Complexity: Viscometers are generally simpler instruments, while rheometers are more advanced, designed for a wider array of materials and flow behaviors.
- Relationship: A rheometer can be considered a more sophisticated viscometer, but a viscometer cannot perform all the functions of a rheometer.
Viscometer vs. Rheometer Range Comparison

Figure 3: A visual comparison of the shear rate ranges of viscometers and rheometers
In essence:
A rheometer is a viscometer, but a viscometer is not a rheometer. The shear rate range of a viscometer is limited, while a rheometer offers a broader spectrum of measurement.
Choosing between a viscometer and a rheometer depends heavily on the material being tested and the specific information needed about its flow properties.
Advertisement
 T&M
T&M