Differential Pressure Flowmeters: Advantages and Disadvantages
Advertisement
Differential pressure flowmeters are a common technology used to measure the flow rate of fluids. They work by creating a constriction in a pipe and measuring the pressure difference across that constriction. This pressure difference is then used to calculate the flow rate. Let’s explore the pros and cons of this technology.
What is a Differential Pressure Flowmeter?
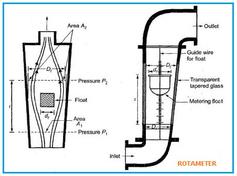
Essentially, a differential pressure flowmeter introduces a deliberate obstruction within a pipe, and measures the pressure variation that occurs as the fluid flows around it. This pressure difference is directly related to the fluid’s flow rate. The beauty of this system is its simplicity and relatively quick development.

A common way to implement this is by inserting a disk or orifice into the pipe. The opening of this orifice is smaller than the pipe’s inner diameter. By measuring the pressure upstream and downstream of the orifice, we obtain the differential pressure, which allows us to calculate the flow.
Benefits of Differential Pressure Flowmeters
Here’s a breakdown of the advantages offered by differential pressure flowmeters:
- Versatile Application: They can handle various fluids, including gases, liquids, and steam.
- Viscosity Measurement: They can also be adapted to measure viscosity.
- Extreme Conditions: They are suitable for use in extreme pressure and temperature environments.
- Adjustable Measurement Range: The measurement range can be modified to suit specific needs.
- No Moving Parts: The absence of moving parts contributes to their robustness and reliability.
- Bidirectional Flow Measurement: They can be configured to measure flow in both directions.
- Wide Range of Sizes: They are available for use in a variety of pipe sizes.
Drawbacks of Differential Pressure Flowmeters
While there are several advantages, it’s important to consider the limitations:
- Limited Span: The relationship between flow rate and differential pressure is a square root function, which can restrict their measurement range.
- Sensitivity to Pressure and Density Changes: Changes in fluid pressure and density can affect the accuracy of the results.
- Not the Most Accurate: They are not the most accurate flow measurement method available.
- Pressure Drop: Orifice plates create a pressure drop within the system.
- Wear and Tear: Although there are no moving parts, the orifice plate can be susceptible to wear. Especially, the sharpness of the edges is crucial, and contamination can lead to inaccuracies.
- Long Inlet and Outlet Sections: They require long inlet and outlet pipe sections for proper operation.
- Expensive Installation: Installing the differential pressure lines, sensors, and fittings can be expensive.
- High Maintenance Cost: They can have a higher maintenance cost.
In conclusion, differential pressure flowmeters offer a simple and versatile solution for measuring flow rates across various applications. However, it is essential to consider their limitations when choosing the right technology for a specific task.
Advertisement
 T&M
T&M