Dry Bulb Temperature vs. Air Temperature vs. Dew Point: Key Differences
Advertisement
Let’s break down the concepts of dry bulb temperature, air temperature, and dew point, and explore how they differ from each other. These terms are all related to the measurement of temperature and moisture in the air, but they each represent a unique aspect of atmospheric conditions.
Dry Bulb Temperature

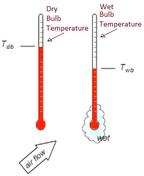
- The dry bulb temperature is what you typically think of as the “air temperature.” It’s the temperature of an air-water mixture measured by a standard thermometer that’s exposed to the air.
- The thermometer is shielded from direct moisture and radiation to get an accurate reading of the air itself.
- We often denote Dry Bulb Temperature as (Tdb)
- For more on this, you can explore the comparison of dry bulb versus wet bulb temperatures.
Air Temperature

- Air temperature is closely related to dry bulb temperature, but it’s crucial to understand its relationship with relative humidity.
- Relative humidity (RH) measures the amount of water vapor in the air relative to the maximum amount it could hold at that specific temperature. It’s expressed as a percentage.
- Interestingly, relative humidity and air temperature have an inverse relationship. When air temperature rises, the relative humidity usually decreases, and vice-versa.
- This means that you often see higher relative humidity at higher altitudes and lower relative humidity at lower ground surfaces. The graph depicted in the original article illustrates this.
Dew Point

- The dew point is a different concept. It’s the temperature to which air must be cooled to become saturated with water vapor, without any change in air pressure.
- When the relative humidity (RH) is high, the dew point is closer to the current air temperature.
- At 100% relative humidity, the dew point and the current air temperature are equal. This means the air is holding the maximum amount of water vapor it can at that temperature and condensation will likely form.
In summary:
- Dry bulb temperature is the standard air temperature we measure.
- Air temperature is directly tied to relative humidity: warmer air can hold more moisture.
- Dew point is the temperature at which the air becomes saturated and condensation begins to form.
Understanding these differences is essential for a variety of applications, from meteorology and climate studies to comfort in our daily lives.
Advertisement
 T&M
T&M