QA vs. QC: Understanding the Key Differences
Advertisement
This article explores the differences between Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC), two crucial components of a robust Quality Management System (QMS). We’ll delve into their definitions and examine how they contribute to overall quality.
Introduction
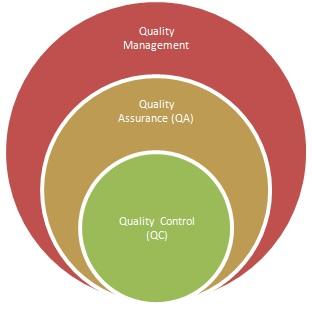
As outlined by ISO standards, every organization should implement a Quality Management System (QMS) to ensure that quality processes are consistently followed. A QMS encompasses various elements, including:
- Quality planning
- Quality improvement activities
- Quality policies
- Quality objectives
- Quality Assurance (QA) procedures
- Quality Control (QC) procedures
There are seven key quality management principles: customer focus, leadership, people engagement, a process-oriented approach, continuous improvement, data-driven decision making, and relationship management.
- ISO 9001, a globally recognized standard within the ISO 9000 family, provides a framework for establishing a QMS. It helps organizations meet customer expectations and achieve other benefits.
- A QMS consists of policies, processes, and procedures essential for planning and executing core business operations.
Quality Assurance (QA)
Definition
Quality Assurance (QA) focuses on establishing quality within the processes used to develop products.
Goal
The primary goal of QA is to create processes that prevent defects from occurring during product development. It’s about building quality into the system, not just checking it at the end.
Examples
- Quality Audit: Regularly assessing processes to identify areas for improvement.
- Verification: Ensuring that processes are followed correctly and meet established standards.
Quality Control (QC)
Definition
Quality Control (QC) concentrates on ensuring quality in the products themselves. QC activities focus on identifying defects in the actual products once they’ve been made.
Goal
QC identifies defects in products before they are released or while still in the production phase. It acts as a final check to catch issues.
Examples
- Inspection and Testing: Examining products to find any flaws or discrepancies.
- Validation/Software Testing: Ensuring that software meets the functional requirements before deployment.
Key Differences: QA vs. QC
The following table highlights the core differences between Quality Assurance and Quality Control:
| Features | Quality Assurance (QA) | Quality Control (QC) |
|---|---|---|
| What is it? | Prevention of quality problems through planned, systematic activities and documentation. | The activities or techniques used to achieve and maintain the product quality, process, and service. |
| As a tool. | It is a managerial tool. | It is a corrective tool. |
| Orientation | QA is process oriented. | QC is product oriented. |
| Who is responsible? | Everyone on the team involved in developing the product. | Specific team(s) test the product for defects. |
| Activities/Processes | Prevent Bug, Plan, and Verify are QA activities. | Detect Bug, Act, and Validate are QC activities. |
| Example | Prevent defects due to quality audits. | Finds defects during testing. |
In essence, QA is proactive, aiming to prevent defects from occurring in the first place. QC is reactive, focusing on finding and addressing defects that already exist. Both are vital for maintaining high quality, and a balanced approach is necessary for success.
Advertisement
 T&M
T&M