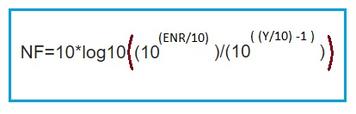Noise Figure Meter: A Comprehensive Guide to Operation and Vendors
Advertisement
This article explains the noise figure meter, its benefits and block diagram, functionality and leading vendors.
Noise Temperature
Passive electronic components inherently generate noise due to the random movement of charge carriers. The higher the temperature, the greater this motion and the resulting noise power. This noise power can be expressed as:
P = K T B
Where:
- K = 1.38 x 10-23 (Boltzmann constant)
- B = Bandwidth
- T = Temperature in Kelvins
Noise Figure
An ideal amplifier wouldn’t add any noise to incoming signals, but real-world amplifiers inevitably do. This added noise can be equated to the temperature of a resistor producing the same amount of noise, termed the “excess noise temperature.” A lower excess noise temperature signifies a better amplifier.
The noise figure (NF) quantifies this noise performance and is defined as the ratio of excess noise temperature to room temperature.
NF = (Te + Tr)/Tr
Ideally, an amplifier should have Te = 0, resulting in NF = 1 (or 0 dB).
Various methods exist for noise figure measurement, including:
- Using noise sources
- Y-factor method
- Signal generator twice power method
- Direct noise measurement method

Noise Figure Meter Operation
Figure 1 illustrates a noise figure meter measuring the noise figure of a Device Under Test (DUT), typically an amplifier or converter.
- Calibration: The noise source is initially calibrated with the noise figure meter.
- DUT Insertion: The DUT is then inserted between the noise source output and the noise figure meter input. The meter then measures the noise added by the DUT.
This method is widely used and highly reliable.
- Down Converter: A down-converter is added at the amplifier’s output if its frequency range falls outside the noise figure meter’s measurement capabilities.
- Pre-Amplifier: An external pre-amplifier is added if the DUT’s output signal is insufficient for accurate measurement.
Noise Figure Meter Vendors and Manufacturers
The following table lists some of the leading vendors and manufacturers of noise figure meters:
| Vendor or manufacturer | Description |
|---|---|
| Keysight Technologies | Model: N8975A , Frequency: 10 MHz to 26.5 GHz |
| Ailtech | Automatic Noise Figure Indicator, Model: 7514 |
| Bruel & Kjaer | 4427 Noise level analyzer |
| Ducommun | Noise figure and gain test set |
Benefits of Noise Figure Meter
Following are some of the advantages of Noise Figure Meter.
- Accurate Noise Measurement : Precisely quantifies the noise figure of amplifiers, receivers, and other RF components to assess performance.
- Optimizes Receiver Sensitivity : Helps in designing low-noise RF front-end circuits, improving overall system performance in communication systems.
- Enhances Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) : Aids in minimizing unwanted noise to ensure clearer signal transmission and reception.
- Essential for RF & Microwave Testing : Widely used in radar, satellite, and wireless communication systems to evaluate component efficiency.
- Supports Design & Development : Crucial for R&D teams working on low-noise amplifiers (LNAs), mixers, and other high frequency components.
- Ensures Compliance with Standards : Helps in meeting industry requirements for noise performance in telecom and defense applications.
- Reduces System Power Consumption : Assists in designing energy efficient RF circuits by optimizing noise characteristics.
- Reliable & Repeatable Measurements : Provides consistent noise figure readings for accurate benchmarking and component comparison.
Conclusion
A Noise Figure Meter is a critical instrument in RF, microwave and communication system testing. By measuring and minimizing unwanted noise, it helps engineers optimize system performance, improve SNR and ensure compliance with industry standards.
Advertisement
 T&M
T&M