Venturimeter: Advantages and Disadvantages
Advertisement
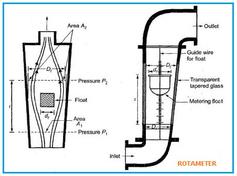
Venturimeters are devices used to measure the flow rate of fluids within a pipe. They operate based on Bernoulli’s principle and can handle various substances like water, other liquids, gases, and even slightly dirty fluids. The size of a venturimeter is typically denoted by its inlet and throat diameters, for instance, a “300 x 150 mm” venturimeter would fit in a 300 mm pipe with a 150 mm throat diameter.

Advantages of Venturimeters
Here’s a breakdown of the benefits of using a venturimeter:
- Low Head Loss: Venturimeters are known for their minimal head loss, typically only about 10% of the differential pressure head. This means they don’t significantly hinder the flow of the fluid.
- High Flow Rate Measurement: They can measure high flow rates in pipes with diameters of a few meters, thanks to their high coefficient of discharge, which results from the lower loss.
- Versatile Positioning: Venturimeters can be installed in any position – whether the pipe is horizontal, vertical, or inclined.
- High Sensitivity: The smaller throat size contributes to higher pressure differentials, which allows for greater sensitivity in measurements.
Disadvantages of Venturimeters
While venturimeters are useful, they also have some drawbacks:
- Space Requirements: Their relatively large size makes them unsuitable for applications with limited space.
- Higher Cost: The larger size of venturimeters also translates to higher manufacturing costs.
- Installation Costs: Due to their size and complexity, the installation of venturimeters can also be more expensive.
- Cavitation Risk: If the throat diameter is too small, it can lead to cavitation within the throat, which can damage the venturimeter and affect measurement accuracy.
 T&M
T&M